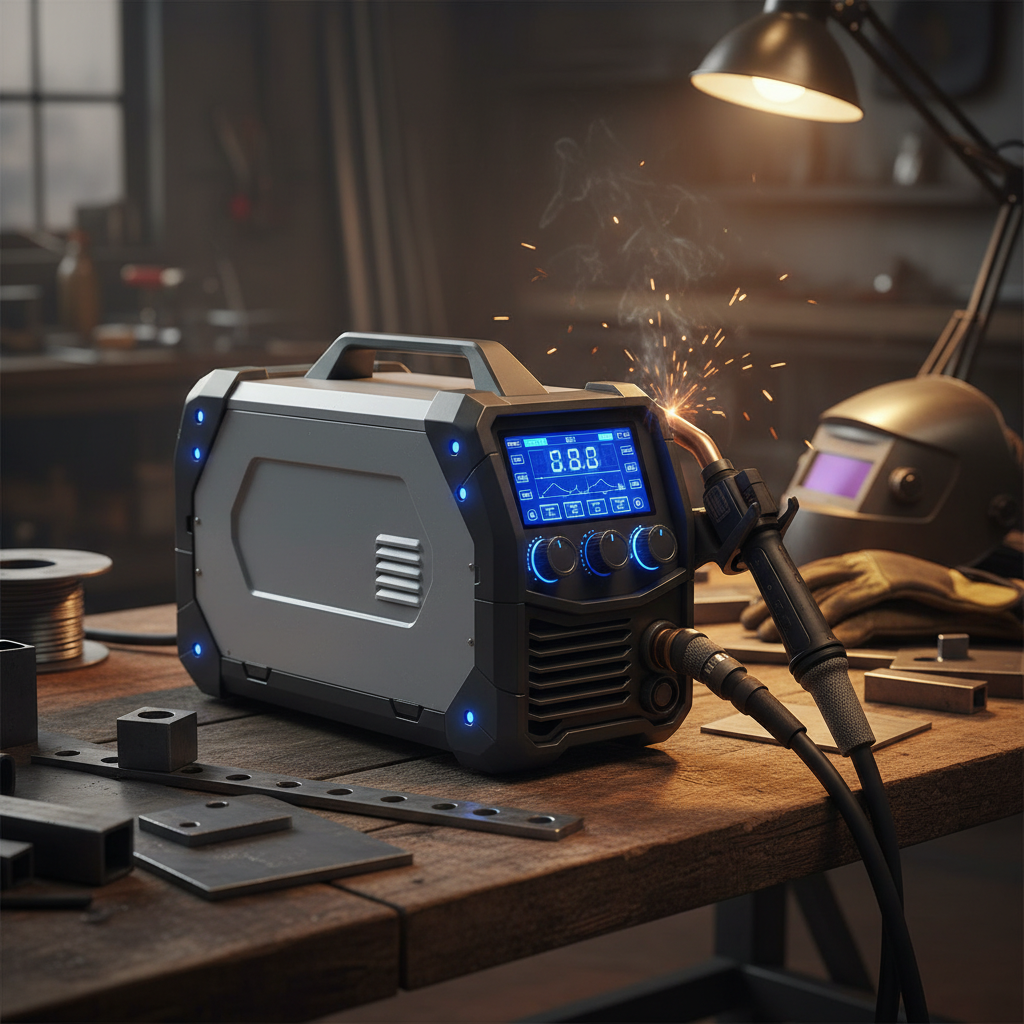
Choosing the right equipment for your welding projects is crucial for ensuring optimal results and efficiency. In recent years, the advancement of technology has led to the introduction of Digital Welding Machines, which offer enhanced features and versatility compared to traditional models. These innovative machines have made it easier for both amateur and professional welders to achieve precise welds with various materials, improving the overall quality of their work.
Choosing the right equipment for your welding projects is crucial for ensuring optimal results and efficiency. In recent years, the advancement of technology has led to the introduction of Digital Welding Machines, which offer enhanced features and versatility compared to traditional models. These innovative machines have made it easier for both amateur and professional welders to achieve precise welds with various materials, improving the overall quality of their work.
When selecting a Digital Welding Machine, it is important to consider several factors, such as the type of welding you will be performing, the power output required, and the machine's portability. The variety of options available in the market can be overwhelming; hence, understanding the specific features of different Digital Welding Machines can help you make an informed decision. From MIG welding to TIG welding, each type has its own set of advantages and is suitable for different applications.
In this guide, we will explore key aspects to consider when choosing a Digital Welding Machine, including top digital types and their functionalities. By the end, you will be equipped with the knowledge necessary to select the best machine for your projects, ensuring that you can achieve professional-quality results every time you weld.
When selecting a digital welding machine, it's essential to consider several key factors that align with your specific needs. First, assess the type of welding you plan to perform. MIG, TIG, and stick welding machines each have different specifications and capabilities. According to the American Welding Society, the demand for MIG welding has surged by over 25% in recent years due to its efficiency in production environments. Therefore, understanding your primary application can help narrow down your options significantly.
Another critical consideration is the power source. Digital welders usually come in AC and DC versions, with DC machines being preferred for multi-purpose tasks, especially for TIG welding. Reports indicate that over 60% of industrial welders favor inverter technology for its lightweight and energy-efficient properties. Additionally, features such as adjustable amperage settings and digital displays can enhance precision and ease of use, making them indispensable for both novice and experienced welders.
Tips: Always check the duty cycle of a machine, as it indicates how long it can run before needing a cooling period. Machines with higher duty cycles are ideal for heavy-duty tasks. Also, consider those with multiple functions to maximize versatility and save space in your workshop. Lastly, read user reviews to gauge reliability and performance in real-world applications before making a purchase.
When selecting the best digital welding machine for your projects, understanding the various digital welding technologies available is crucial. Each type of welding technology serves specific applications, making it essential for users to assess their project needs. Among the notable types are arc welding, resistance welding, gas fuel welding, and solid-state welding. Arc welding, widely popular for its flexibility and effectiveness in joining metals, utilizes an electric arc to produce heat. In contrast, resistance welding is primarily used for mass production in automotive and manufacturing industries, where low-cost and high-speed applications are necessary.
Additionally, the welding consumables market plays a significant role in this selection process. Understanding the types of consumables—such as electrodes, solid wires, and flux-cored wires—is vital in determining compatibility with different welding processes. As industries increasingly demand high-quality, efficient welding solutions, knowing how these consumables fit with various welding technologies can help users choose the right machine that enhances productivity, reduces costs, and meets project specifications effectively.
| Welding Technology | Description | Common Applications | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIG Welding | Metal Inert Gas welding, uses a continuous wire feed. | Automotive, fabrication, and thin materials. | Fast, easy to learn, and versatile. | Less effective on rusty or dirty metals. |
| TIG Welding | Tungsten Inert Gas welding, uses a non-consumable tungsten electrode. | Aerospace, automotive, and high-quality seams. | Precise control over heating, and great for thin materials. | Slower process and requires skill to master. |
| Stick Welding | Uses a consumable electrode coated in flux. | Construction and maintenance on rusty or dirty materials. | Works well outdoors, portable and effective. | Produces more slag and requires clean-up. |
| Flux-Cored Arc Welding (FCAW) | Similar to MIG welding but uses a tubular wire filled with flux. | Heavy machinery and structural fabrication. | Effective in windy conditions, high deposition rates. | Requires significant clean-up of slag and spatter. |
| Electron Beam Welding (EBW) | Uses a beam of high-velocity electrons in a vacuum. | Aerospace and advanced manufacturing. | High penetration and speed, minimal thermal distortion. | Requires expensive equipment and maintenance. |
When selecting the best digital welding machine for your projects, it's essential to conduct a comparative analysis of various models based on their features, costs, and performance metrics. Begin by evaluating the machine's technology, such as inverter vs. transformer models, as this can significantly impact efficiency and portability. Look for features like multi-process capability, which allows the machine to handle different welding techniques, from TIG to MIG, and consider additional functions like advanced control systems and digital displays for enhanced user experience.
**Tips:** When comparing models, pay attention to the duty cycle specifications. A higher duty cycle indicates the machine can operate longer before needing to cool down, making it suitable for prolonged projects. Additionally, consider the cost of replacement parts and ease of maintenance, as these factors can contribute to your project's overall expenses and efficiency.
Another important aspect is the performance metrics, including arc stability and weld quality. Read customer reviews and expert assessments to gauge user satisfaction and reliability. Don't hesitate to test a few machines if possible; hands-on experience can help determine which one feels right for your specific needs.
**Tips:** Always have an idea of the thickness of materials you plan to weld; some machines are better suited for thin sheets, while others excel at thicker materials. Matching the machine to your project requirements is key to achieving successful results.
When selecting a digital welding machine, it's crucial to evaluate several essential specifications to ensure it meets your specific project needs. One of the primary considerations is the machine's amperage range. Adequate amperage allows the welder to work on various materials, from thin sheets to thicker metal sections. Additionally, pay attention to the duty cycle rating, as this indicates how long the welder can operate before needing to cool down. A higher duty cycle is preferable for extended projects, ensuring consistent performance without overheating.
Another critical factor is the machine’s versatility in terms of welding processes. Digital welding machines often offer multiple functions such as MIG, TIG, and stick welding. This adaptability can be a significant advantage, allowing for various applications and skill levels. Furthermore, consider the user interface and control options; a digital machine with an intuitive display and easy-to-adjust settings can enhance usability and precision.
Finally, ensure that the machine meets relevant industry standards, which can guarantee safety and reliability in demanding environments. By carefully evaluating these specifications, you can select a digital welding machine that is well-suited for your projects.
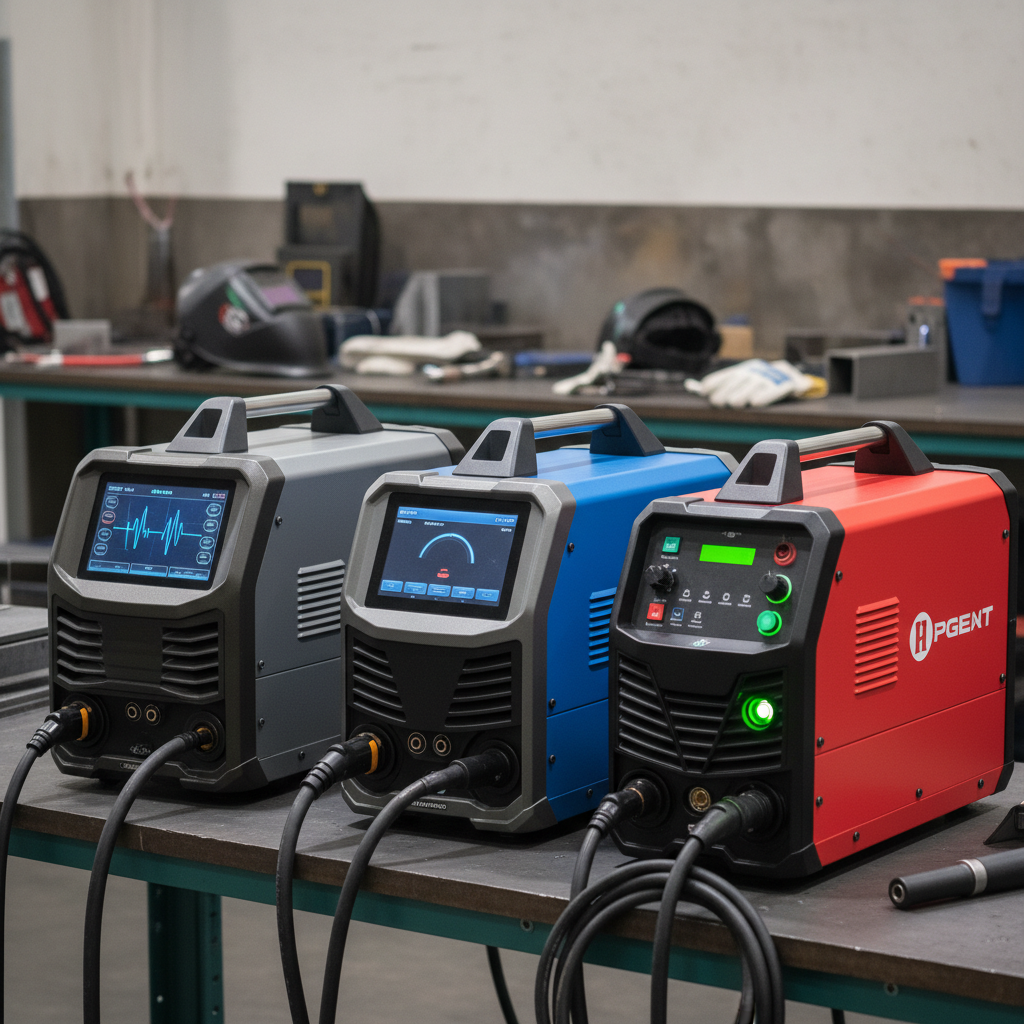

When selecting a digital welding machine, it’s crucial to consider the top brands in the market, as they significantly influence customer satisfaction and user experience. Leading brands like Lincoln Electric, Miller Electric, and Hobart dominate the digital welding machinery segment, thanks to their commitment to quality and innovation. These manufacturers have established strong market shares by continuously improving their technology and providing reliable support services, making them trusted choices for both professionals and hobbyists.
Customer satisfaction ratings play a vital role in assessing the effectiveness of these machines. Research indicates that brands like Lincoln Electric often receive high marks for their durability and ease of use, which are critical factors for many welders. Similarly, Miller Electric's machines are praised for their advanced features, offering users a balance of performance and control. By focusing on the market share and customer feedback, potential buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring that they choose equipment that not only meets their project demands but also enhances their welding experience.