Choosing the right inverter welding machine can significantly impact your welding projects, whether you are a professional welder or a DIY enthusiast. Inverter welding machines have gained popularity due to their portability, efficiency, and ease of use. With a wide range of models and features available on the market, selecting the most suitable machine for your specific needs can be a daunting task.
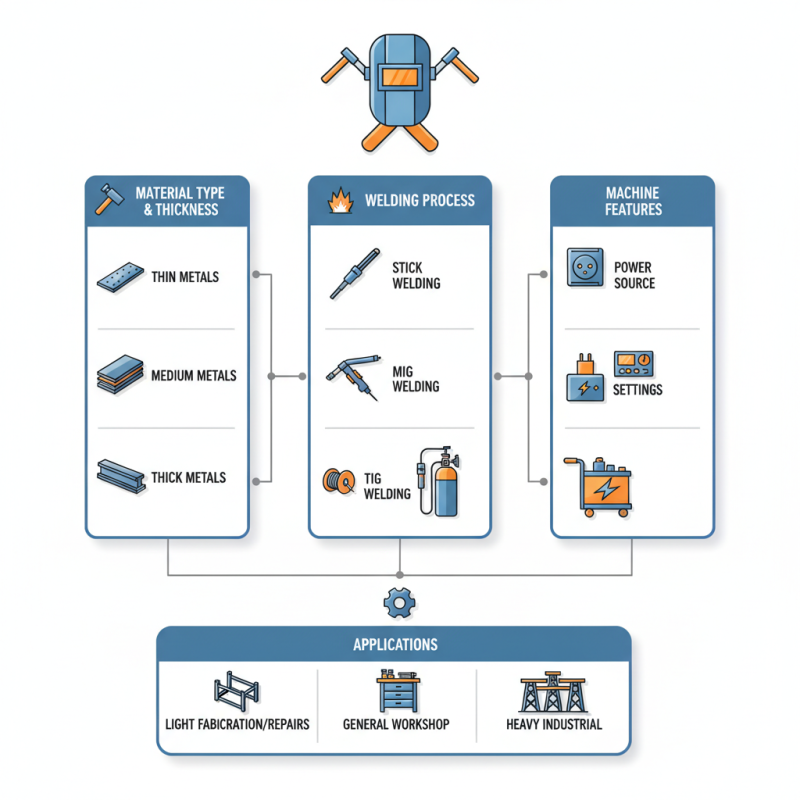
Understanding your requirements is crucial when evaluating different inverter welding machines. Factors such as the type of materials you will be working with, the thickness of those materials, and the welding processes you intend to use must be considered. Furthermore, you should be aware of the power source, settings, and portability of the machine, as these elements can greatly influence the effectiveness and convenience of your welding tasks.
In this guide, we will explore key considerations and features to look for while choosing an inverter welding machine. Whether you are seeking a machine for light fabrication, repairs, or heavy-duty industrial applications, this information will help you make an informed decision that aligns with your specific welding needs.

When selecting an inverter welding machine, several key considerations can significantly influence your decision. Firstly, understanding the type of welding processes you will perform is crucial. According to the ARC Welding Market Analysis published by Research and Markets, the demand for inverter welding machines is projected to grow at a CAGR of 4.5% from 2021 to 2026, indicating a robust market trend driven by the versatility of these machines in multiple welding techniques, such as MIG and TIG welding. This versatility makes them ideal for both hobbyists and professionals.
Another pivotal factor is the machine’s amperage range, which directly affects the thickness of materials you can weld. Inverter welders typically offer a wide range of amperage settings, often between 10 to 500 amps, catering to various applications from thin sheet metal to heavy-duty welding. Additionally, features like portability and ease of use, often highlighted in industry reports, are essential—especially for fieldwork. Inverter machines are generally lighter and more compact than traditional models, allowing welders to work efficiently in various environments. Therefore, carefully assessing these factors can lead to selecting the right inverter welding machine tailored to your specific needs.
When selecting the right inverter welding machine, it's crucial to understand the different types available on the market. Inverter welding machines are primarily classified into three categories: TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas), MIG (Metal Inert Gas), and Stick welders. According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the global welding equipment market is projected to reach USD 30.68 billion by 2026, indicating an increasing demand for high-quality and efficient inverter machines.
TIG welding is renowned for its precision, making it ideal for intricate work and materials such as stainless steel and aluminum. Conversely, MIG welding is popular for its speed and ease of use, making it suitable for larger projects and thick materials. Stick welders, on the other hand, are celebrated for their versatility and performance in outdoor conditions. Knowing these distinctions can help you select the right machine based on your project requirements.
Tips: Consider the power requirements and portability of the machine. A 110V inverter is perfect for hobbyists, while a 220V machine is better for professional applications. Also, ensure you check the duty cycle, as it indicates how long the machine can operate before it requires a cooldown. This is crucial for maintaining efficiency during extensive welding projects.
When selecting the right inverter welding machine, evaluating power requirements and output specifications is crucial. The power output of an inverter welder is typically measured in amperes (A), and understanding your specific welding tasks can help determine what range of amperage is needed. For instance, light gauge metal welding may only require 20 to 90 A, while heavier applications, such as MIG welding on thicker materials, might necessitate machines that can deliver between 150 to 300 A. According to the American Welding Society, ensuring that your inverter welding machine matches your maximum and minimum amperage needs can significantly enhance your welding efficiency and output quality.
Additionally, power source compatibility is essential. Most inverter welding machines operate on single-phase or three-phase power, affecting their efficiency and portability. A report from the Welding Equipment Manufacturers Committee indicates that inverter technology not only reduces the weight of the machine but also enhances the power-to-weight ratio, making it more suitable for both on-site and shop applications. It is also important to assess the duty cycle—expressed in percentage—of the machine, which indicates how long you can operate it continuously before needing to allow it to cool down. For example, a machine with a 60% duty cycle at 200 A can operate for six minutes out of ten, influencing your overall work productivity. Thus, a careful evaluation of these specifications ensures that you choose an inverter welder that meets your specific needs and enhances your welding capabilities.
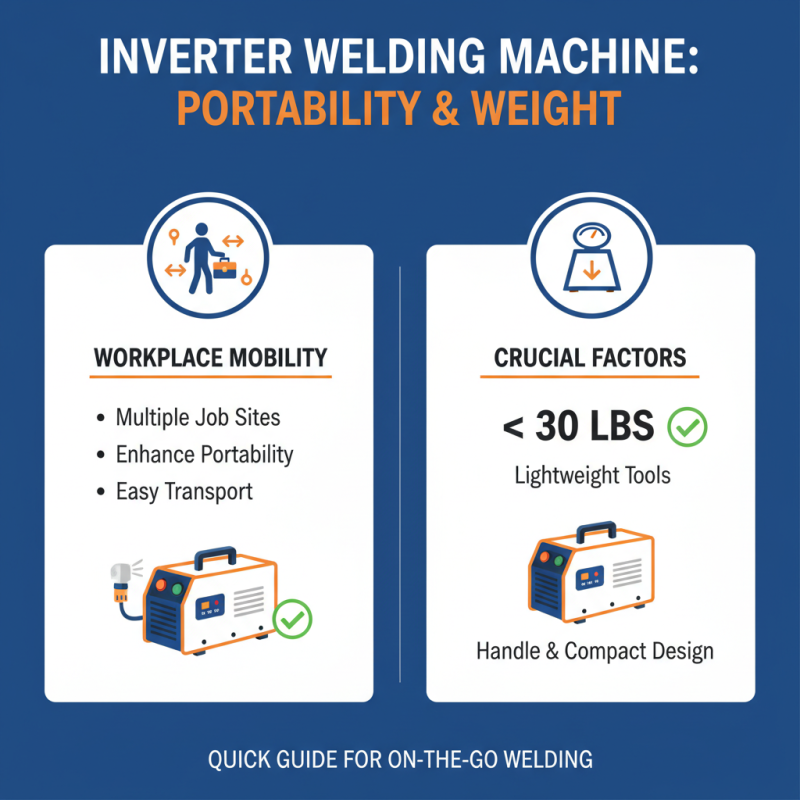
When selecting an inverter welding machine, assessing portability and weight is crucial for accomplishing your welding projects effectively. If you frequently work at various job sites, a lightweight and portable inverter welding machine can significantly enhance your mobility. Tools that weigh less than 30 pounds are generally easier to transport, making them ideal for those who need to travel between locations. Additionally, consider the design of the welding machine; options with handles or compact cases are more convenient for on-the-go tasks.
Moreover, the portability of a welding machine also impacts its functionality. A compact design often means it can fit into tighter spaces, making it versatile for diverse projects, from car repairs to construction work. It's essential to ensure that while the machine is lightweight, it does not compromise on power or performance. Investing in a model that balances portability with the capability to handle the welding tasks you require will enable you to work more efficiently. Ultimately, understanding the specific demands of your projects will guide you in selecting the perfect inverter welding machine for your needs.
When selecting the right inverter welding machine for your needs, it’s essential to consider various additional features and technologies that can enhance your welding experience. Modern inverter welders come equipped with a range of functionalities that cater to different welding processes, such as MIG, TIG, and Stick welding. This multi-process capability ensures versatility, allowing you to tackle various projects without needing multiple machines. For instance, some advanced models provide seamless transitions between welding types, which can significantly simplify workflow and increase efficiency.
Moreover, features like adjustable output settings and advanced control systems enhance precision and performance. Some inverter welders also incorporate inverter technology, resulting in better efficiency and portability compared to traditional welders. The ability to handle different materials and thicknesses while maintaining consistent results is crucial for professional outcomes. It's essential to inspect these additional features carefully, as they can greatly impact the overall usability and effectiveness of the welder you choose, ensuring it meets your specific welding needs.
| Feature | Description | Importance Level |
|---|---|---|
| Power Output | Measure of the machine's welding capacity, typically in Amperes | High |
| Duty Cycle | Percentage of time the welder can operate continuously without overheating | High |
| Weight | Weight of the machine; important for portability | Medium |
| Input Voltage | Voltage requirement for the inverter welder, e.g., 110V or 220V | High |
| Control Technology | Smart technology features like digital displays and advanced settings | Medium |
| Safety Features | Includes thermal overload protection, anti-stick, and other safety measures | High |
| Welding Processes | Types of welding supported, such as MIG, TIG, or Stick welding | High |