The Flux Core Welder is a crucial tool in various industries. It provides efficient welding for construction, manufacturing, and repair work. According to the American Welding Society, the demand for skilled welders is projected to grow by 8% from 2020 to 2030. This increase highlights the importance of understanding welding technologies, including flux-cored arc welding.
Flux Core Welders use a continuous tubular wire filled with flux to shield the weld pool. This process allows for effective welding in windy conditions and on dirty surfaces. Despite its advantages, it requires careful handling. Controlling heat and preventing spatter can be challenging for novice welders. It’s essential to practice and refine techniques to achieve high-quality welds.
In an industry that thrives on precision, the learning curve can be steep. Many beginners face issues such as incomplete fusion or excessive slag. A Flux Core Welder can be forgiving, yet it demands respect and attention to detail. Those who invest time in mastering this tool often find it immensely rewarding. Understanding the mechanics of the Flux Core Welder is key to success in today’s competitive job market.
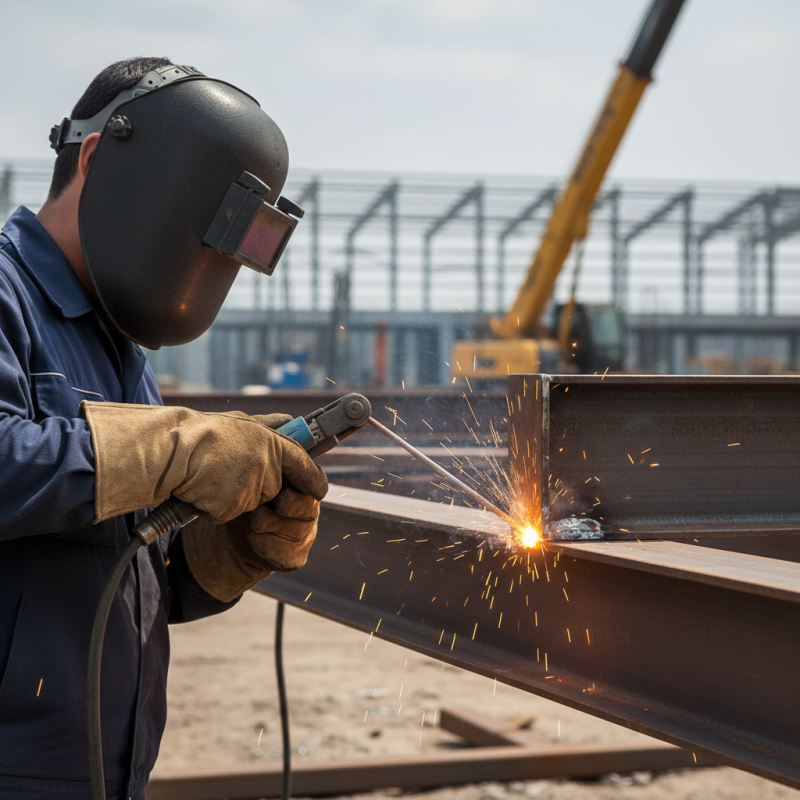

Flux core welding is a unique process that utilizes a tubular wire filled with flux. This wire acts as both the electrode and the shielding gas. As the welder creates an arc, the heat melts the metal and the core of the wire. The flux then vaporizes to provide gas coverage, protecting the weld pool from contaminants in the air. This makes flux core welding versatile, especially in outdoor conditions.
One significant advantage of flux core welding is its ability to work without a separate shielding gas. It simplifies the setup and makes it portable. However, this process has its challenges. The slag produced can be difficult to remove, requiring additional effort post-welding.
New welders often struggle with controlling the speed and angle, leading to inconsistent welds. Mastering the technique takes practice and patience. While the process is efficient, there’s always room for improvement and learning from mistakes.
A flux core welder is a popular tool for welding applications. It has several key components that make it effective. The most critical part is the welding gun. This is where the welding wire is fed. It also includes a nozzle that helps direct the shielding gas and heat.
The welder's wire is filled with flux. This flux creates a protective gas when heated. It helps prevent contamination from the surrounding air. The welder also has a power source that provides the necessary electrical current. This current melts the wire and joins the metals together.
Tips: Check your setup regularly. Look for any signs of wear. Keeping your equipment maintained ensures smooth operation.
Another important component is the ground clamp. It completes the electrical circuit and provides a stable welding arc. A poor ground connection can cause problems, like weak welds. It's crucial to ensure a secure connection.
Tips: Always clean the surface before welding. Dirt and rust can weaken bonds. Taking time to prep can save headaches later.
Remember, practice is essential. Not every weld will be perfect. Learning from mistakes helps improve your technique. Embrace the process and keep experimenting with your flux core welder.
A flux core welder uses a unique process for joining metals. It relies on a continuous wire filled with flux. The flux acts as a shielding agent during the welding process. When the wire is heated, it melts, and the flux creates a protective gas shield. This is vital for preventing contamination from the surrounding air.
Operating a flux core welder requires a steady hand. The welder moves the torch along the joint. This requires practice to maintain a consistent speed. If the speed is too fast, the weld may be weak. If it's too slow, it can create excessive heat, leading to warping. The process can be messy. Spatter and slag can occur, which may decrease efficiency and quality.
Understanding the settings on the welder is key. Voltage and wire feed speed must be adjusted based on material thickness. It’s also essential to choose the right flux core wire type. Each type has its strengths and weaknesses. Learning from mistakes is part of improving your skills. Even experienced welders revisit the basics to refine their technique.
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Welding Process | Uses a continuous hollow filler wire and flux to protect the weld from contamination. |
| Power Source | Typically powered by a DC or AC welding machine designed to supply the necessary voltage and current. |
| Portability | Flux core welders are often portable, making them suitable for fieldwork and outdoor applications. |
| Applications | Commonly used in construction, repair work, and metal fabrication due to their versatility. |
| Advantages | Good for welding outdoors, minimal shielding gas required, and can weld thicker materials. |
| Disadvantages | Produces more slag, requires cleanup, and can create a less aesthetically pleasing weld compared to solid wire welding. |
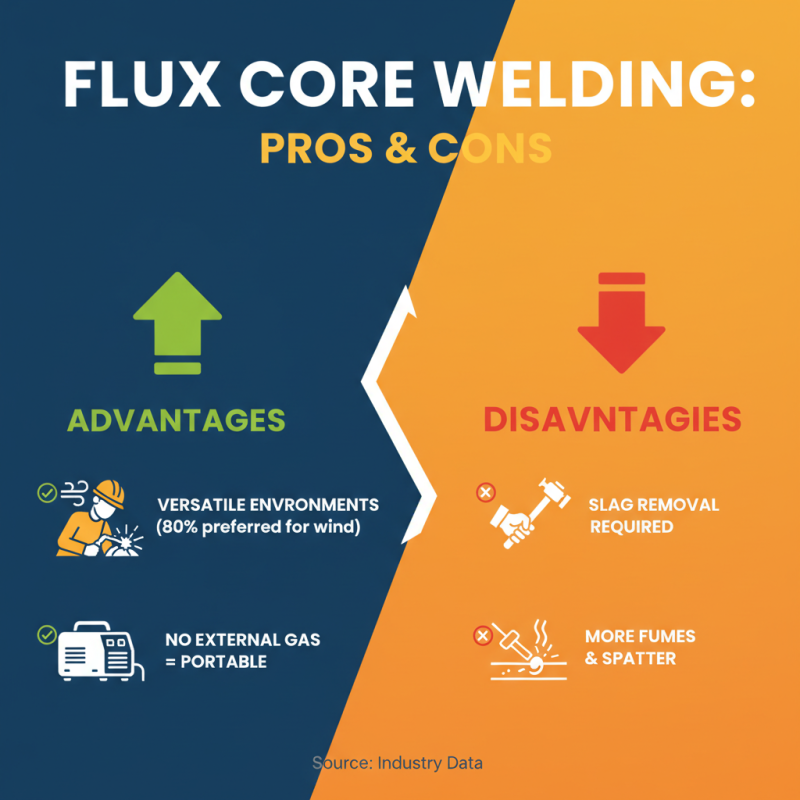
Flux core welding, known for its versatility, presents both advantages and disadvantages. One major advantage is its effectiveness in various environments. Data suggests that about 80% of professionals prefer flux core welding for projects exposed to wind. This makes it ideal for outdoor work, especially in construction. The self-shielding capability of flux core wires eliminates the need for external shielding gas, boosting portability and convenience.
However, there are downsides to consider. The slag produced can lead to additional cleanup work, which is often overlooked. Some users report that the welds require extra sanding and cleaning, particularly in aesthetic projects. Moreover, the process can generate more smoke and spatter compared to traditional MIG welding. An estimated 40% of welders find this aspect bothersome, affecting visibility and indoor applications. The need for a protective mask becomes even more critical. Balancing these pros and cons is essential for welders seeking efficiency while maintaining quality.
Flux core welding is widely used across various industries. It offers speed and flexibility, making it suitable for both indoor and outdoor projects. Construction sites often utilize this technique for building structures. It can join thick materials quickly. This efficiency makes it a favorite among fabricators as well.
In the automotive sector, flux core welding plays a crucial role. It is essential for repairing vehicles and constructing frames. The ability to work in windy conditions is a significant advantage. However, the quality of the welds can be inconsistent. This can lead to problems if not monitored closely.
Shipbuilding is another industry where flux core welding shines. The process allows for fast, strong welds. Additionally, it can be applied to various metals. Yet, the potential for slag and spatter remains an issue. Welders must continuously adapt to the challenges of this method. Overall, while flux core welding has its advantages, careful attention is needed to ensure quality outcomes.






