In the realm of welding, Smaw Stick Welding has emerged as one of the most versatile and widely used techniques. According to the American Welding Society, over 60% of welders utilize Smaw in various industrial applications, highlighting its significance in the welding landscape. This manual arc welding process is known for its adaptability to different positions and environments, making it a preferred choice in sectors ranging from construction to manufacturing. Moreover, a report by IBISWorld indicates that the demand for welding services has expanded, with a projected growth rate of 3.1% annually in the next five years, further emphasizing the need for skilled welders proficient in Smaw Stick Welding techniques. Mastering these techniques not only enhances performance but also boosts efficiency, reducing costs and increasing workplace safety. As such, a focused approach to honing Smaw Stick Welding skills is essential for both novice and experienced welders aiming to stay competitive in this evolving industry.

SMAW, or Shielded Metal Arc Welding, is a fundamental technique in the welding industry that combines efficiency with versatility. At its core, SMAW involves an electric arc formed between a consumable electrode and the workpiece, which melts both the electrode and the base metal to create a strong bond. Understanding the fundamental principles of this process is crucial for any welder aiming to enhance their skills and achieve optimal performance.
One of the key aspects of SMAW is the selection of the right electrode, which is determined by the materials being welded, the desired penetration, and the specific welding position. Each electrode has unique properties and applications, making it essential to match the electrode with the job requirements. Additionally, mastering the technique of maintaining the correct travel speed, arc length, and angle can dramatically improve the quality of the weld. Practicing these fundamentals not only leads to proficient welding but also ensures safety and efficiency on the job.
To excel in SMAW stick welding, welders should focus on developing hand-eye coordination and control, as these skills significantly impact the consistency of their welds. Regular practice, combined with a strong understanding of the principles behind the process, fosters confidence and precision. By honing these foundational skills, welders can elevate their craft and achieve remarkable results in their welding projects.
| Technique | Description | Tip for Mastery |
|---|---|---|
| Electrode Selection | Choosing the right electrode type and size for the material being welded. | Consult the AWS chart for appropriate electrode selection based on materials. |
| Arc Length Control | Maintaining the correct distance between the electrode and the workpiece. | Practice to find that optimal distance to avoid excessive spatter. |
| Travel Speed | The rate at which the welder moves the electrode across the joint. | Perform test welds to adjust speed for smoother beads. |
| Joint Preparation | Proper cleaning and fitting of the joint can affect weld quality. | Ensure that surfaces are free of contaminants. |
| Welder Positioning | Proper posture and angle for the best access and control. | Adjust your stance for comfort and stability during the weld. |
When it comes to stick welding, having the right equipment and tools is crucial for achieving optimal performance and efficiency. Essential gear includes a quality welding machine, electrodes, and personal protective equipment (PPE). According to the American Welding Society, stick welding remains one of the most widely used techniques across various industries, thanks in part to its versatility and effectiveness in outdoor environments where wind and contamination can pose challenges for other welding methods.
Investing in a reliable welding machine, such as an inverter-based model, can significantly enhance your welding capabilities. These machines provide better arc stability and efficiency, allowing for lighter and more portable setups. Additionally, selecting the appropriate electrodes—such as E6011 for general-purpose work or E7018 for structural applications—can impact weld quality and performance. A study by the Lincoln Electric Company shows that choosing the right electrode can result in a 20% increase in productivity and a reduction in defects.
Moreover, protective gear cannot be overlooked. High-quality welding helmets, gloves, and protective clothing not only ensure the welder's safety but can also prevent distractions during the welding process. Data from the Occupational Safety and Health Administration indicates that adhering to safety standards and using proper PPE can lead to a 30% decrease in work-related injuries. By prioritizing the right equipment and tools, welders can achieve not only better quality welds but also a more efficient and safer working environment.
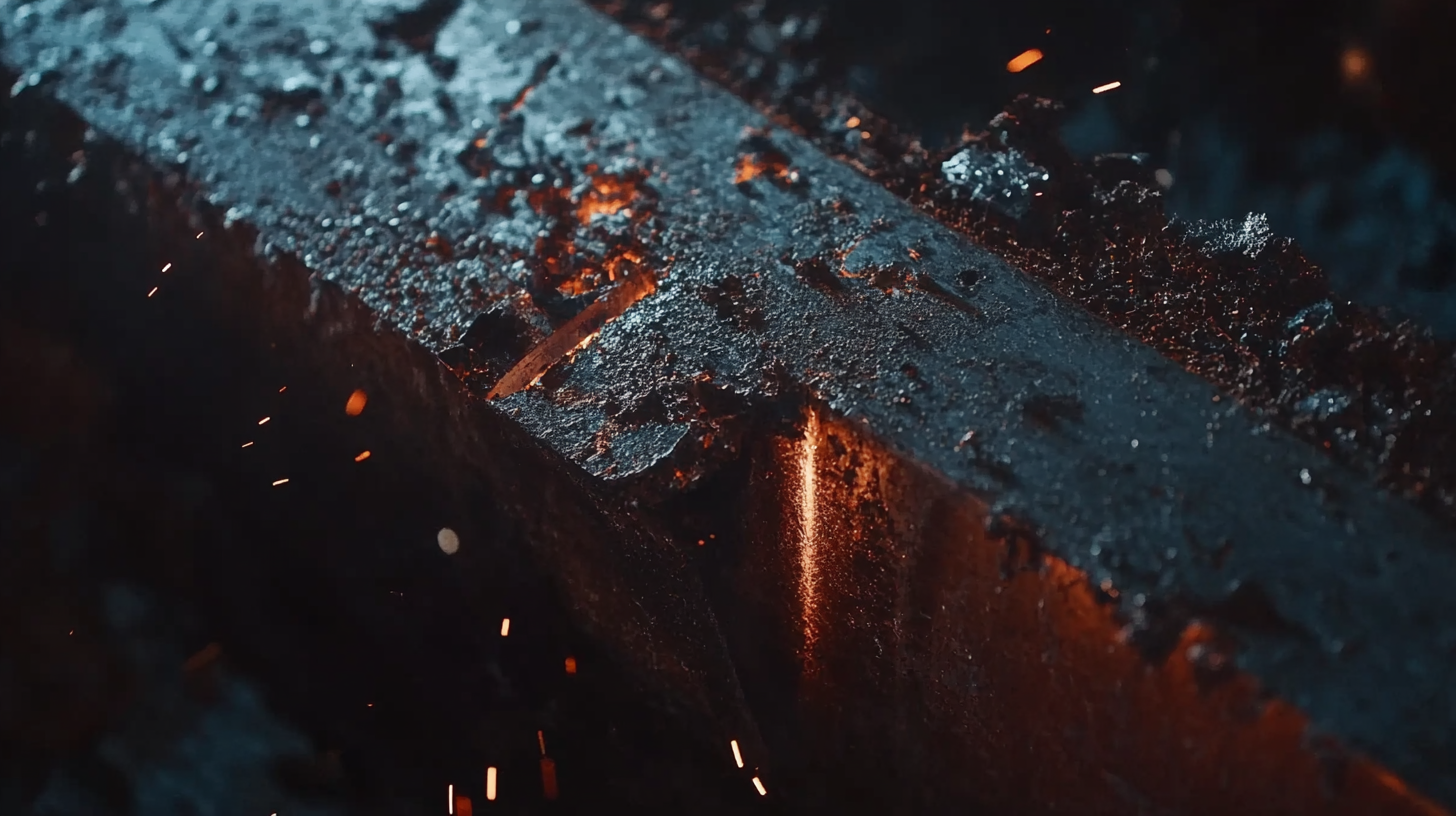
Mastering SMAW (Shielded Metal Arc Welding) stick welding techniques requires an understanding of heat control and material penetration to achieve optimal performance. Effective heat management is crucial, as excessive heat can lead to distortion in the workpiece and affect the weld quality. A welder’s ability to adjust the arc length and travel speed plays a significant role in controlling heat input. By practicing dynamic adjustments and using different electrode angles, welders can better manage the heat, ensuring a more refined and controlled bead profile.
Furthermore, material penetration is another vital factor that influences the strength and durability of the weld. Ensuring proper penetration involves selecting the right electrode diameter and type for the material being welded. Using the correct travel speed and weave pattern enhances penetration depth while promoting good fusion with the base metal. By applying these techniques, welders can improve joint integrity, leading to stronger and more reliable welds, especially when working with varying material thicknesses or more challenging welding positions.
As the field of welding evolves, incorporating advanced inspection techniques like X-ray Computed Tomography (micro CT) may further enhance quality control in welding applications. This method allows for the examination of internal weld integrity without compromising the structure, ensuring that the techniques employed yield a product that meets industry standards. This fusion of traditional skills and modern technology signifies a leap towards greater efficiency and performance in SMAW stick welding.
SMAW (Shielded Metal Arc Welding) is a popular welding technique, but many welders encounter common pitfalls that can affect their efficiency and the quality of their work. One of the most frequent mistakes is improper electrode handling. Wet or contaminated electrodes can lead to weak welds and might even cause arc instability. It's vital to keep electrodes dry and free from any contaminants before starting the welding process. Additionally, regularly checking for the correct angle and arc length during welding can significantly improve the overall quality of the weld.
Another common error is neglecting to maintain a consistent travel speed. Uneven speed can result in uneven weld bead appearance and penetration. To avoid this, welders should develop a steady rhythm, allowing the molten metal to flow smoothly and bond effectively. Practicing on scrap materials can help build muscle memory for maintaining that consistent pace. Moreover, not adjusting the amperage settings based on the material thickness can lead to undercut or excessive burn-through. Being mindful of these adjustments will make a significant difference in achieving optimal weld quality.

Mastering SMAW (Shielded Metal Arc Welding) techniques requires a focus on achieving consistent weld quality and appearance. As the industry evolves, integrating advanced technology into the welding process has become essential. For instance, recent advancements in laser vision seam tracking technology have paved the way for improved precision and stability in welds. This innovation allows welders to adjust in real-time, significantly reducing the margin for error and enhancing the overall quality of welds. In fact, it’s reported that with this technology, manufacturers can achieve up to 30% reduction in rework costs due to better initial weld quality.
To ensure consistent results in SMAW, welders should pay attention to variables such as electrode type, arc length, and travel speed. Utilizing the appropriate electrode can result in optimal penetration and bead appearance. Industry data indicates that using the correct electrode can improve deposition rates by as much as 25%, leading to both efficiency and superior weld aesthetics. Additionally, maintaining a steady travel speed is vital; an inconsistent movement can lead to irregular bead shapes and potentially detrimental slag inclusions.
With the integration of modern technologies and methodical approaches in training, welders can not only improve their craft but also adapt to the growing demands of the industry. Techniques like laser tracking can complement traditional SMAW methods, elevating the standards of quality in welding practices across various manufacturing sectors.
This chart illustrates the weld quality scores of various SMAW stick welding techniques, highlighting the effectiveness of each method. Consistent use of high-scoring techniques can lead to improved weld quality and overall performance.
